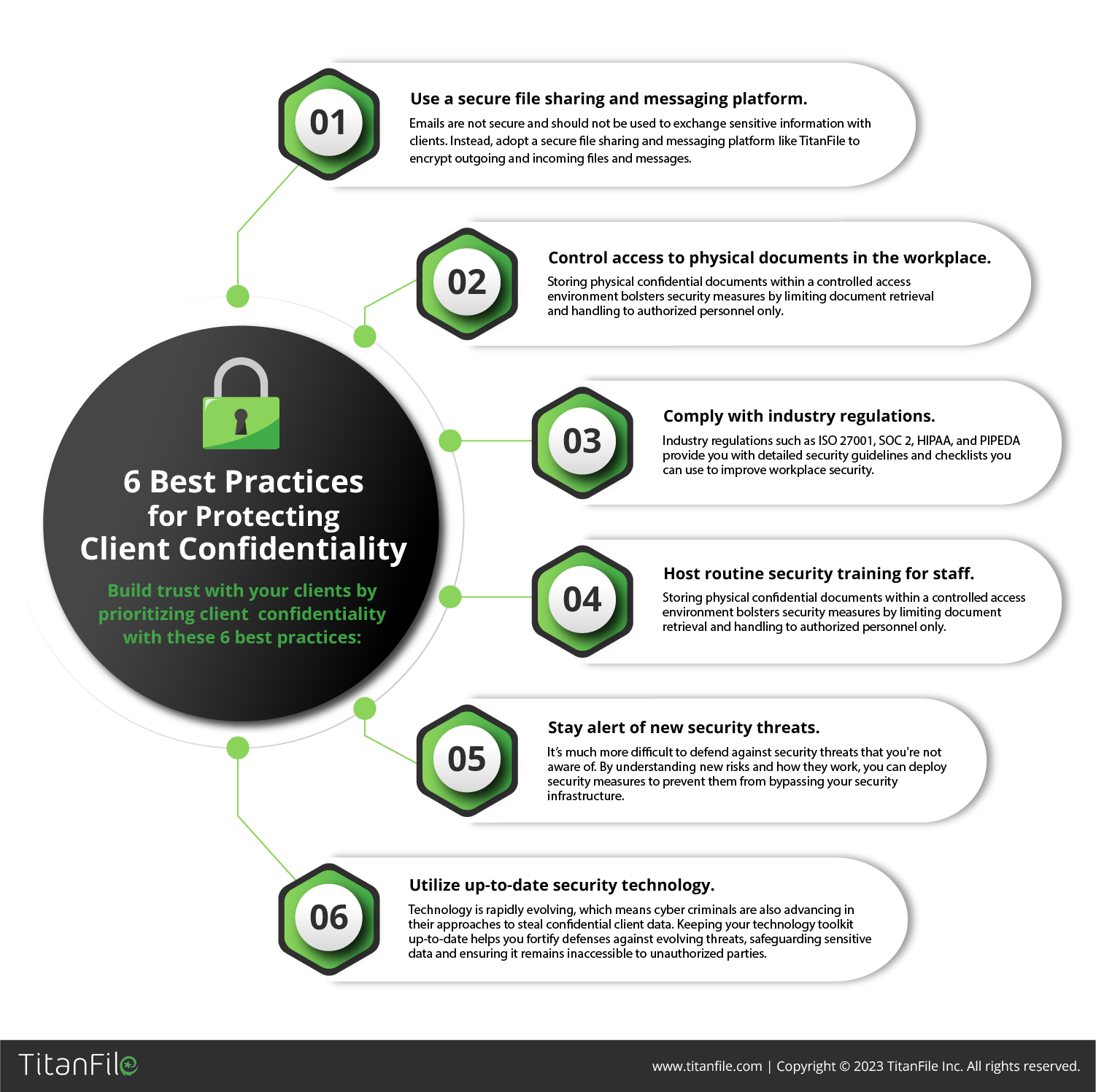
Maintaining the confidentiality of records is a fundamental aspect of safeguarding sensitive information and upholding trust in various sectors. To safeguard people, organizations, and even society as a whole, it is essential to maintain the confidentiality of all data, whether it be personal, financial, or business-related.
The importance of maintaining record confidentiality will be discussed in this article, along with the consequences of breaches and preventative steps that can be taken to safeguard sensitive data.
What is Confidentiality?
Confidentiality stems from the word “confine.” Confidentiality itself is the process of keeping confidential documents secure from those who do not have authorized access.
Every business demands confidentiality as they have confidential work and client documents that needs to be protected. In additon, it’s important to abide by the confidentiality rules set by your government.
What Does Confidential Data Include?
It’s essential to understand what information or data comes under confidentiality. The data that is non-public comes under confidential records. For example:
Individual data:
- Social Security / Social Insurance numbers
- Vehicle identification numbers (VINs)
- Medical and health records
- Credit card numbers
- Banking details
- Passwords and usernames
- Addresses
Company data:
- Personal employee information
- Financial records
- Business plans
- Research data
- Customer data
These are just the tip of the iceberg. Any information that, if leaked, can harm an individual or an organization should be kept confidential.
Examples of confidential information
Here are some examples of confidential information in different industries:
- Healthcare: Protected Health Information (PHI) under HIPAA
- Legal: Case files, discovery materials, privileged communications
- Accounting: Client tax filings, audit documentation, and financial disclosures
- Government: Classified documents, regulatory reports, citizen data
Protecting this kind of sensitive information requires demands the right tools. TitanFile is your trusted solution for secure file sharing and client collaboration. It is trusted by professionals in the legal, healthcare, and financial sectors to keep confidential data safe, compliant, and under control.
Here’s how it works:
Why is Confidentiality Important?
Why is it important to maintain the confidentiality of your company’s and clients’ records and information? Understanding the significance of confidentiality is essential for your organization.
Maintaining and keeping clients’ documents confidential is needed in today’s high-tech era. A breach of confidentiality can lead to serious repercussions such as identity theft, fraud, harm to one’s reputation, and compromised privacy.
In a nutshell,
- Confidentiality helps build your employees’ and clients’ trust in your company.
- If you are from the medical industry, confidentiality promotes confidence. Patients are more prone to talk to their doctors when they know their information will stay locked behind doors.
- High confidentiality eliminates the chance of misuse of data and sensitive information.
- Confidentiality keeps the company’s reputation intact. Clients are more likely to work with companys that prioritize the protection of their data.
- Confidentiality keeps the company records and information from the wrong hands; this is highly important when employing staff for sensitive positions like research departments.
What Type of Information Must or Should Be Protected?
Legal (Lawyers, Paralegals, Legal Support Staff)
- Client case files and court documents
- Attorney-client privileged communications
- Contracts and discovery materials
- Litigation strategies and internal memos
- Evidence files, including medical or financial data
Healthcare (Doctors, Clinics, Hospitals)
- Patient medical records and diagnostic reports
- Medical conditions
- Insurance and billing information
- Appointment notes, prescriptions
- Mental health or treatment disclosures
Accounting & Finance (CPAs, Advisors, Bookkeepers)
- Tax returns
- Financial statements
- Payroll and employee records
- Investment portfolios and client transactions
- Business valuations
- Audit findings
Education (Teachers, Admin Staff, Counsellors)
- Student academic records and performance reports
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs)
- Disciplinary history and incident reports
- Family or guardian contact details
Types Of Confidentiality
There are five main types of confidential information. In your workplace, you must be familiar with these types of confidentiality in order to safeguard your company and client data.
1. Employee/Staff Information
Anything related to your employees must be regarded as confidential, from gossip to personal information. Especially if you are in the management or HR department, handling such information sensitively is crucial.
Employee’s personal information, such as name, address, maiden name, etc., should be kept in secure files. These shouldn’t be attached to unsecured emails and shouldn’t be passed through unsecured communication channels. It is how data leaks happen.
Apart from securing the company’s reputation, you are also required by the law to keep such information confidential.
2. Administrative Information
Administrative information means all decisions that the executive department makes for the employees. It means promotions, redundancies, hiring of new employees, as well as pending disciplinary actions against employees. All this is confidential and illegal to share with third parties without prior consent.
3. Organizational Information
Organizational information is most commonly known as the trade secrets of a company. Such information is highly crucial for any company’s success or failure. This data includes the company’s private information, such as policies and processes, budget information, costs, forecasts, and customer contact information.
4. Customer/Contact Information
In sensitive jobs like research and financial departments of companies, the employees have to sign Non-disclosure agreements; these also come under trade secrets. Moreover, the customer’s information in organizations like banks and call centers is also confidential.
5. Professional Information
Personal information given to any individual or practicing professional (lawyers, doctors, accountants, etc.) is confidential. Leaking such information can result in legal action by the affected individual.
Challenges in Maintaining Confidentiality
Today, most organizational data is stored and shared electronically via emails, cloud drives, internal messaging platforms, and external storage devices. While these systems increase convenience, they also introduce new risks.
In Q3 of 2024 alone, over 422 million data records were exposed in global data breaches, highlighting the growing threat to sensitive information.
The global cost of cybercrime is projected to surge to $13.82 trillion by 2028.
One of the biggest obstacles is file sharing. Most email platforms and cloud tools limit file size, leading employees to use insecure workarounds like personal email accounts, USB drives, or unencrypted links.
The average office worker sends around 40 emails a day. With that volume, it’s easy to make a mistake or fall victim to threats like:
- Phishing attacks disguised as legitimate file requests
- Accidental sharing of confidential attachments or links
- Sending files to the wrong recipients
- Weak password protection or outdated access controls
- Lack of audit trails to track who accessed sensitive files
- Use of unauthorized apps or personal accounts to bypass file size limits
- No way to retract or secure files after they’re sent
TitanFile solves these challenges by giving professionals a secure, encrypted environment to send messages and large files of any size without ever leaving their inbox.
Titanfile replaces email attachments with secure channels, enforces access controls, provides real-time tracking, and ensures full compliance with regulations like HIPAA, PIPEDA, and GDPR. Customers can opt for data residency in Europe, Canada or the U.S.
Dietrich Law faced similar challenges in maintaining confidentiality when dealing with large, sensitive files. By switching to TitanFile, the firm eliminated insecure email practices to opt for a more compliant way to exchange confidential healthcare documents. Today, they send and receive critical information securely, without friction or risk.
“TitanFile is flexible, reliable, and has enabled us to send and receive confidential healthcare documents while meeting any concern for security.”
– George Dietrich, Managing Lawyer at Dietrich Law
What is a breach of confidentiality?
Confidentiality breaches occur when sensitive, protected, or private information is accessed, disclosed, or shared without authorization.
It may violate compliance obligations (like HIPAA, PIPEDA, or GDPR), trigger lawsuits, result in financial penalties, and cause irreparable harm to reputation. Even one mistake can erode years of client trust and brand equity.
A data breach can have severe consequences, such as:
- Identity theft and financial fraud
- Legal action and class-action lawsuits
- Regulatory fines and sanctions
- Loss of customer loyalty
- Operational disruption and crisis response costs
Examples of a Breach of Confidentiality
Below are some high-profile breaches that highlight the consequences of poor data protection:
- PowerSchool Breach (2025): A 19-year-old exploited internal vulnerabilities in PowerSchool’s customer support system, stealing the sensitive data of tens of millions of students, teachers, and administrators. This highlights the risks of poor access controls in education systems.
- National Public Data Breach (2024): A background check firm was hacked, exposing nearly every U.S. citizen’s Social Security numbers and sensitive records. The breach led to public outrage, lawsuits, and increased calls for data handling and storage standards reform.
- 23andMe (2023): Through credential stuffing attacks, hackers gained access to the genetic and personal data of roughly 6.9 million users, exposing insights on ancestry, health traits, and predispositions.
- Vastaamo Psychotherapy Center (Finland, 2020): Hackers accessed sensitive mental health records and tried to extort both the clinic and its patients. Approximately 30,000 individuals were affected in what became one of Europe’s most disturbing breaches of medical confidentiality.
How can you respond to a security breach at work?
When a breach occurs, how you respond is just as important as the breach itself. A slow or disorganized response can increase damage and further undermine trust. Here’s how to respond effectively:
- Contain the breach immediately: Identify the source of the breach and cut off further unauthorized access. This might include disabling accounts, revoking access, or taking systems offline temporarily.
- Notify your internal response team: Alert your IT, compliance, and legal teams so they can begin assessing the impact and preparing mitigation plans.
- Document everything: Maintain a detailed log of what happened, when it was discovered, how it was addressed, and who was informed.
- Communicate with stakeholders: If required, notify affected clients, regulatory bodies, or third parties promptly and transparently. Honest communication helps rebuild trust and avoid legal issues.
- Conduct a post-breach review: Analyze the root cause and determine what went wrong, such as technical gaps, human error, or process failure.
- Strengthen systems and retrain staff: Update policies, patch vulnerabilities, and reinforce secure file-sharing practices against potential breaches.
Every organization that handles sensitive information should have a clear confidentiality policy. This policy outlines which types of information are confidential, who has access, how it should be managed, and the consequences of mishandling it.
Organizations must combine strong data policies with ongoing employee training. Confidentiality training should cover identifying sensitive information, using secure tools, and avoiding risky work behaviours.
One Reddit user advised: “Tell whoever is above you, present the evidence, and let them decide what to do.”
TitanFile is a secure file-sharing and client collaboration solution that helps employees maintain workplace confidentiality with enterprise-grade encryption. All activities are logged, allowing administrators to monitor who accessed what information and when. This helps prevent and investigate data breaches.
Conclusion
Breaches of confidentiality can be detrimental to your business. It’s important to keep all such data under high security.
If you need a secure way to share confidential information, TitanFile is the best solution for secure file sharing. TitanFile encrypts data both in transit and at rest, preventing leaks during sharing or while stored.
Organizations in legal, financial, healthcare, government, and medical trust TitanFile to maintain the confidentiality of their records.